Author: Amanda Stanger, Indigenous Programs Manager
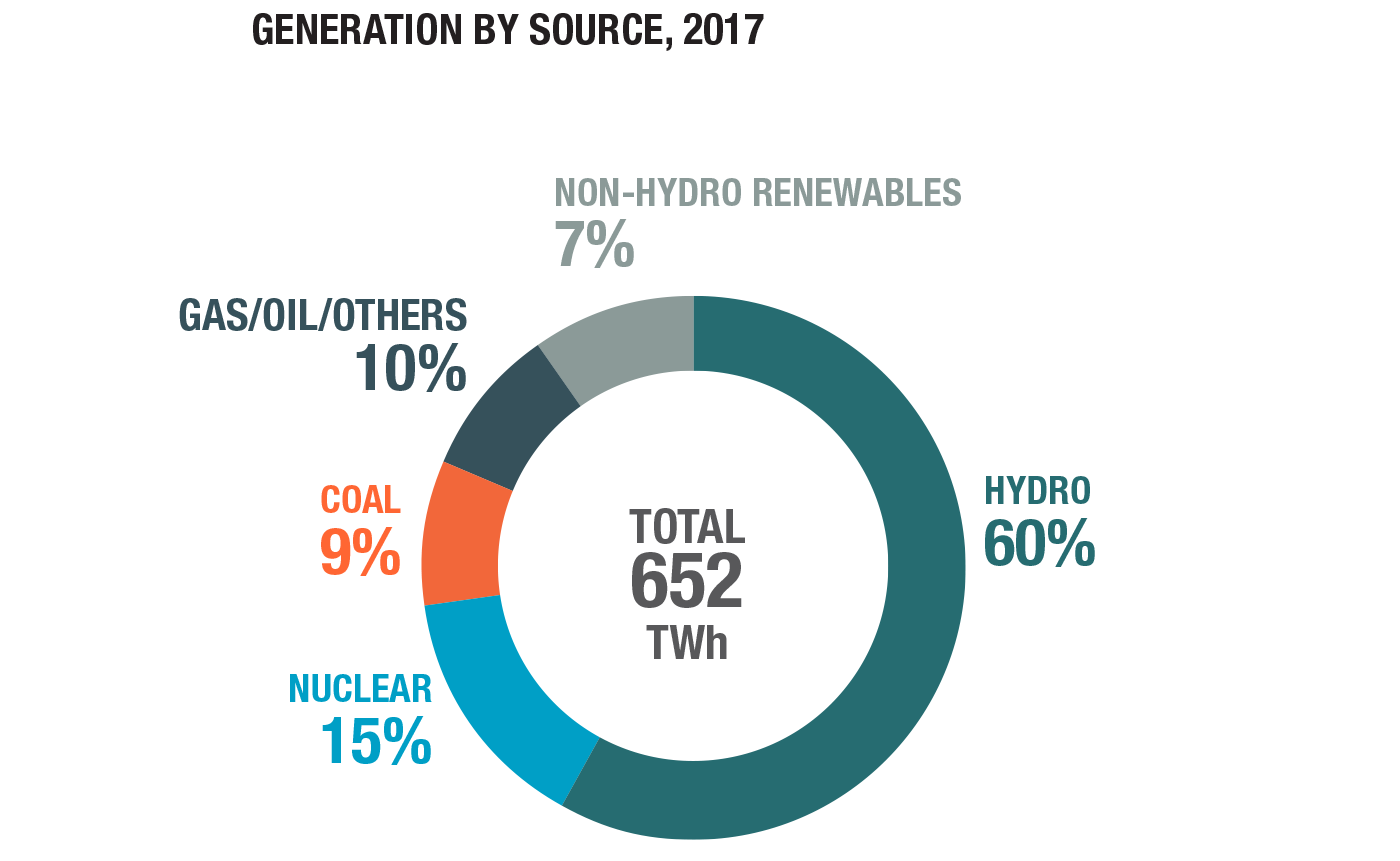
Electricity is called “Hydro” by many Canadians, which is a short-form for hydro-electricity. That’s because most of the electricity generated is by using hydro dams. But, due to our population and energy demands, we also have to use alternative sources of power.
What kind of power production is there and what’s used across Canada?
All across Canada, there are different kinds of electricity generation; here are the three most widely used sources of electrical power.
Renewables: Hydro, Solar, Wind, Tidal, Geothermal and Biomass
Did you know that renewable energy powers more than half of our homes and businesses in Canada? Renewable energy generation is a more natural process of creating electricity that replenishes at a rate that is equal or faster than the rate at which electricity is consumed. There are many different forms of renewable energy, such as directly or indirectly from the sun (solar), or from heat generated deep within the earth, called geothermal. Renewable energy sources currently provide about 67% of Canada’s total energy supply. Moving water is the most important renewable energy source in Canada, providing 60% of Canada’s electricity generation. In fact, in 2018, Canada was the third largest producer of hydro-electricity in the world.
The other 7% of renewable energy generation in Canada is generated from solar, wind, biomass, geothermal and ocean resources, solid biomass, biogas and liquid biofuels. Wind and solar energy are the fastest growing sources of electricity in Canada.
Nuclear
Did you know that in order to create nuclear power, uranium is needed? After raw uranium is mined and milled, it is processed to make fuel for nuclear reactors to generate electricity. Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions that release nuclear energy to generate heat. Canada is the second largest producer and fourth exporter of uranium in the world. The United States is the first. 15% of Canada’s electricity was attributed to nuclear energy in 2018. Nuclear power is a source of energy that does not emit greenhouse gases. Canada has developed a unique nuclear reactor technology, called CANDU. Under Canada’s nuclear non-proliferation policy, Canadian uranium can only be used for peaceful purposes.
Diesel and Coal
They are not clean energy, but they are available in remote areas of Canada. In many cases diesel is the only available option for power since Canada’s north is not connected to the electricity grid. Diesel and coal use in Canada provides about the 10% of electricity generation in Canada. Diesel is expensive and very noisy as diesel generators clatter and rumble. It is also unreliable. More commonly with the increase of extreme weather conditions, importing diesel has been delayed or even cancelled leaving many communities forced to fly in diesel at a cost in millions, which many communities cannot afford, or alternatively they are left in the dark and have to evacuate hospitals and local occupants.
Most of Canada’s population lives in the southern parts of Canada that are connected to the grid, leaving us to often take for granted what life would be like without easy access to electricity.
Main photo of electrical generation graph is from NRCAN’s website